Get Avast One to protect yourself against phishing attacks and other threats
- Security
- Privacy
- Performance
Think you can spot a scam? Spear phishing attacks are devilishly deceptive. Designed to look like legitimate emails, spear phishing campaigns can fool even the savviest among us. Read on to learn about spear phishing attacks and how to avoid them, then protect yourself with Avast One, ironclad security software with intelligent threat-detection capabilities.

Spear phishing is an email or electronic communications scam that targets specific individuals or groups with the goal of getting them to reveal personal information or infecting their devices with malware. Spear phishing attacks are designed to appear like legitimate emails from familiar or well-known sources.

This Article Contains:
After identifying a target individual or group (like an organization or business), an attacker crafts and sends a message, usually via email, purporting to come from a trusted and familiar source.
The email or message is meticulously designed to appear real and fool even the most perceptive recipients. The phony email tries to convince the victim to reveal personal data, and usually it contains a link to a well-disguised website that asks for personal information or is riddled with malicious software.
Here’s how a spear phishing attack works:
An attacker identifies a particular person or piece of data they want.
The attacker researches the victim to find a way to gain trust or contact them in an authoritative way.
The attacker “spears the phish,” usually via email, convincing them to reveal the info/data they want.
Though similar, the difference between phishing and spear phishing is how the two attack vectors target victims. Phishing works by targeting large groups of people with broad scams that are often easy to detect. Spear phishing scams, by contrast, target select individuals or groups with personalized attacks that can appear strikingly authentic.
Generally, in the battle of spear phishing vs phishing, the former is more dangerous because it’s more targeted and deceptive. Since spear phishing focuses on select groups, the attack is well-researched and carefully carried out, making it difficult to detect.
A far cry from the well-known and rather generic “Nigerian prince” scams, cybercriminals use spear phishing for highly intentional attacks on specific individuals in order to access particular information, such as the numerous Apple ID phishing scams that can be hard to spot.
Similar to spear phishing, whaling is a phishing attack that targets powerful employees in a company — like CEOs, CFOs, or other executives — in order to gain sensitive and valuable information. Whaling refers to the size of the “catch” — high-profile employees or celebrities.
Another particularly deceptive practice is pharming. Unlike phishing, pharming attacks manipulate traffic from real websites, redirecting victims to fraudulent sites that install malware or steal sensitive personal information.
All these different kinds of attacks target potential victims through various forms of social engineering, like using fake emails and websites, constructing phony social media profiles, posing as respected or authoritative sources, etc. Since these threats can come in many forms, digital literacy is essential to prevent them.
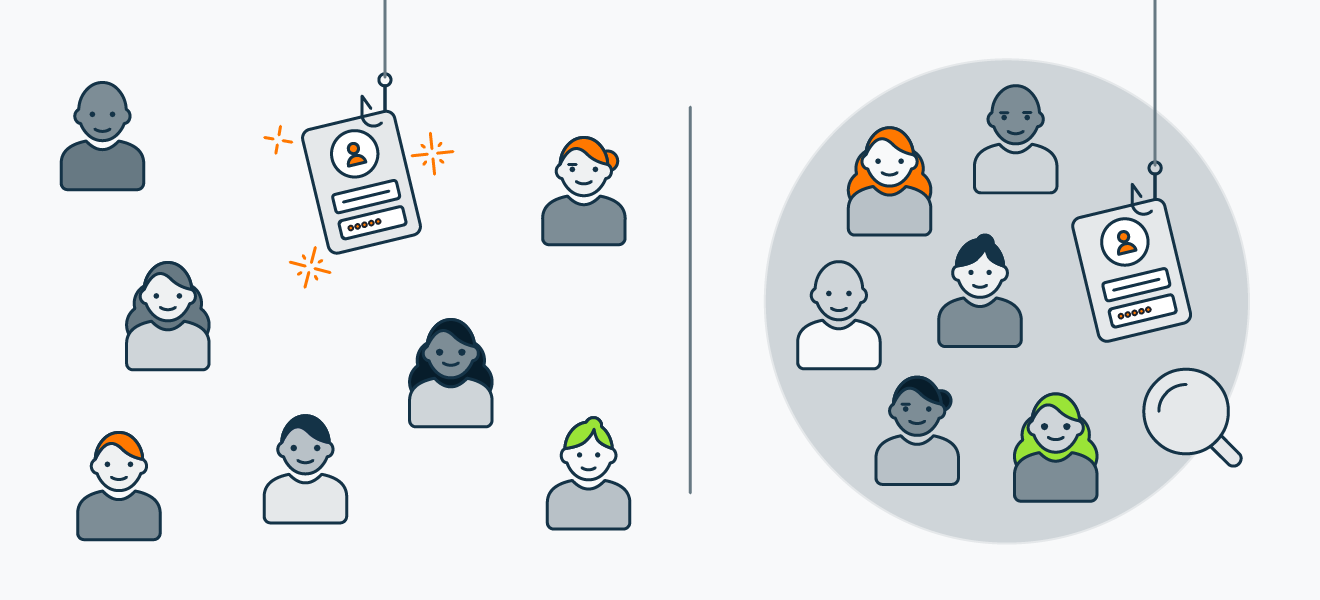 Phishing targets anyone and everyone, while spear phishing targets specific people or groups.
Phishing targets anyone and everyone, while spear phishing targets specific people or groups.
Because a spear phishing attack is tailored to particular individuals or groups, they are highly-calculated to appear like they’re from trusted sources. Like a double agent in a thriller — equipped with disguises and fake passports — a lot of effort goes into a spear phishing scam. Here’s how a spear phishing attack works:
An attacker identifies and researches a victim: Because spear phishing attacks are so targeted, research is needed to identify potential victims and create effective scams. Like other forms of identity theft, social media is often used to find victims, gather contact details, and craft a scam based on personal information.
A personalized message is crafted to fool the victim: The more personalized the scam message, the more convincing it will be. Cybercriminals use spoofing and other tools informed by their research to deceive potential victims. Attackers can design fake emails with the same look and feel as legitimate companies. And because the attacks are crafted with key details about the victims, they’re more successful.
After trust is established, the victim is hooked (speared): It’s easy to fall prey to spear phishing attacks because the well-researched emails build trust. Scams are often unsuccessful and easy to spot when they’re broad. Because of the personal touch, victims overlook spear phishing scams. Lured by the bait, they follow links leading to phony sites where they give away personal information or download malware, like a keylogger.
To help create spear phishing scams, attackers can buy information about potential victims on the dark web. Personal and valuable information often ends up for sale on the dark web after it’s leaked in a data breach or other hack.
Some of the biggest names in tech, politics, and pop culture have fallen victim to spear phishing scams, with far-reaching consequences. Here’s a look at some of the most famous spear phishing examples.
Does a tweet from Amazon founder Jeff Bezos, promising to send you bitcoin, sound too good to be true? How about a similar tweet from Elon Musk or Kanye West? In 2020, Twitter revealed that hackers took over 45 high-profile twitter accounts with spear phishing campaigns.
Over the course of several hours, hackers used these accounts to tweet out a basic bitcoin scam: victims were promised double the amount of bitcoin they sent to a specific bitcoin wallet linked in the tweets. And because the scam came from the verified accounts of influential people, it was successful.
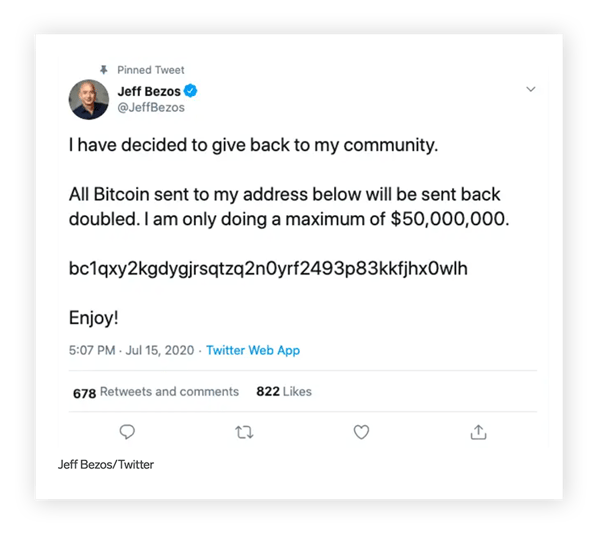 This successful spear phishing attack caught Jeff Bezos in its net.
This successful spear phishing attack caught Jeff Bezos in its net.
A post-mortem press release by Twitter said the hackers used “phone spear phishing” techniques to pose as IT workers and trick Twitter staffers into giving out credentials that gave the hackers access to an internal company tool. This tool let them reset the passwords and two-factor authentication setups of the targeted accounts.
Politicians often have top-level security detail on hand wherever they go, but that doesn’t stop cybercriminals. 2016 was a rough year for the American Democratic party: just prior to losing their bid for the US presidency, they fell victim to a highly-targeted spear phishing campaign.
As a result of the spear phishing attack, thousands of emails from Democrat staffers were leaked, including personal information about top party leaders like Hillary Clinton and Bernie Sanders. These emails contained sensitive and damaging details that were used against them by their opponents and the media alike. Some argue it influenced the results of the election.
Hackers scammed the Democrats by creating a fake Gmail account and sending emails claiming there was unusual activity on their network and urging the staffers to change their passwords by clicking a link. The rest is political history.
Spear phishing attacks are effective because unlike broad, low-tech scams, they’re highly-targeted and well-researched. Spear phishing attacks use personal information against victims to create convincing scams.
Spear phishing attacks effectively play on your emotions. There’s almost always a sense of urgency in the messaging — prompting victims to “act quickly before it’s too late.”
In a spear phishing attack, hackers use any info that makes the attack more convincing. We share so much online these days — our emails, job titles, social and professional networks, and much more — and all of it can be used to sculpt a highly persuasive spear phishing scam.
Spear phishing is highly effective, but you can minimize the fallout by guarding your information, and taking other steps to prevent identity theft.
Another way to avoid the dangerous waters that spear phishers hunt in is to use strong and secure antivirus software. Avast One offers six layers of air-tight protection against even the most deadly threats. Plus, our free software features an intelligent antivirus system that detects and blocks phishing attacks — along with viruses, spyware, ransomware, and other forms of malware.
Prevention is your best weapon against spear phishing attacks. Hackers rely on the inattentiveness of their victims, so spotting their tricks will neutralize the threat. You can also ensure your safety with a few time-honored strategies for beefing up your cybersecurity.
Here’s how to prevent a spear phishing attack:
Education and awareness. Practice good cyber hygiene by not clicking on strange links, not sharing your passwords, not oversharing on social media, and learning to identify suspicious emails.
Email security software. Supplement your know-how with software that protects your devices. The best antivirus software can detect and block incoming phishing attacks, as well as a host of other cyberthreats, like malicious email attachments, spyware, and ransomware attacks.
Strong passwords. Computer passwords protect everything from online bank accounts to social media to email — so stolen or leaked passwords can cause serious trouble. Use strategies to create strong, complex passwords. And use a password manager to create uncrackable passwords for all of your accounts.
Backups. No matter how careful you are, you still might get hacked. If you have to fully restore your system, have a clone of your hard drive or a backup of all your files via USB, external hard drive, or cloud storage.
Updated software. Hackers are constantly improving their methods and applying new technology. That’s why it’s crucial to regularly update your software and apply new security patches to plug holes and block exploits.
Verified email. If you receive a suspicious email, find a safe and secure online email checker to verify the address. There are many options available, but like anything you download, be sure to research its legitimacy beforehand. Plus, use multi-factor authentication on your email and social media accounts for another layer of protection.
Spear phishing attacks are subtle and even experts can be duped. A watchful eye on suspicious emails and other communications is your best prevention strategy.
But to stop threats that slip past you, robust antivirus software like Avast One is crucial. Our Intelligent Antivirus feature detects and blocks phishing ploys along with other cyberthreats. And it’s powered by one of the largest threat-detection networks in the world, so you’ll always be protected against the latest threats.
With powerful and comprehensive protection and a sleek interface, Avast One is quite the catch!
Install free Avast One for Android to block phishing attacks and get real-time protection for your phone.
Install free Avast One for iOS to block threats and get real-time protection for your iPhone or iPad.
Download free Avast One for PC to block phishing attacks and get real-time protection for your Windows computer.
Download free Avast One for Mac to block phishing attacks and get real-time protection for your Apple computer.
Get Avast One to protect yourself against phishing attacks and other threats
Get Avast One to protect yourself against phishing attacks and other threats